Chapter goals
- Being familiar with the basic requirements of life.
- Being able to explain the structures of animal and plant cells.
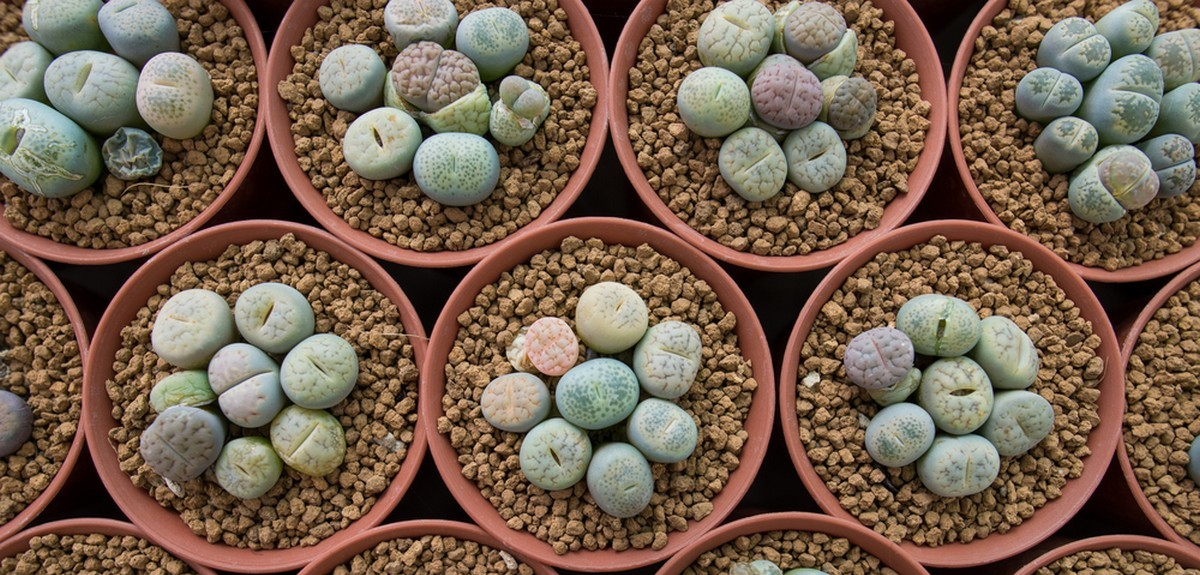
Pebble plants (also known as living stones) are plants that can be found in the dry areas of Southern Africa. As their name suggests, they look very much like small stones. This makes it hard to distinguish between these plants and the stones that surround them. However, pebble plants are living organisms, whereas the stones that surround them are lifeless.

What kinds of things does life need in order to exist? The existence of life requires:
There can be no life without energy. Energy is needed to make different things happen. All life on planet Earth receives most of its energy from the Sun.
Plants, algae and some bacteria are capable of photosynthesis. This means that they can make use of the energy contained in sunlight to produce chemical energy. Photosynthetic organisms store this energy in chemical compounds. All other living organisms are dependent on the chemical energy produced by these organisms.
The solar energy bound by green plants and other producers moves through the food chain and is used by consumers, such as herbivores and predators.
All life on planet Earth is organic. This means that it is based on different carbon compounds. Carbon is an element that can easily form different kinds of molecular structures, such as chains and wheels.
When carbon chains are joined together with different elements, such as hydrogen, nitrogen or oxygen, the result is an organic compound. Living organisms need and create these kinds of compounds, which include carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. In addition to the elements and compounds listed above, living organisms also need other elements in order to thrive. These elements include phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and iron.

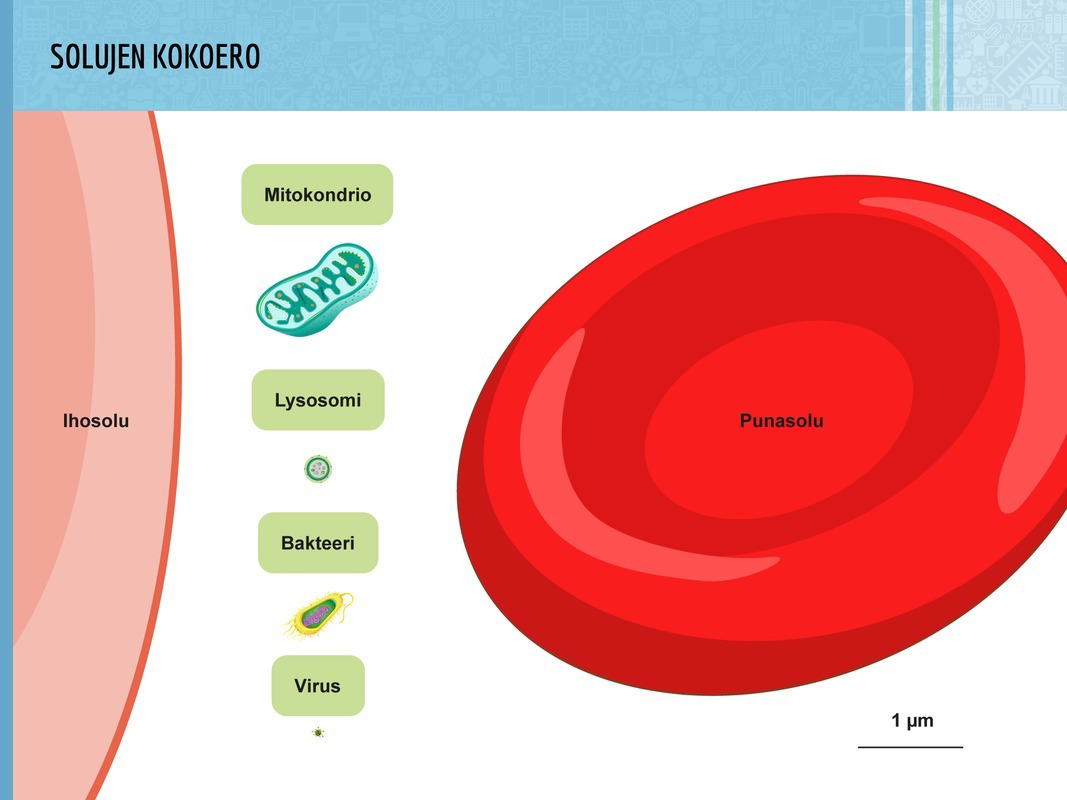
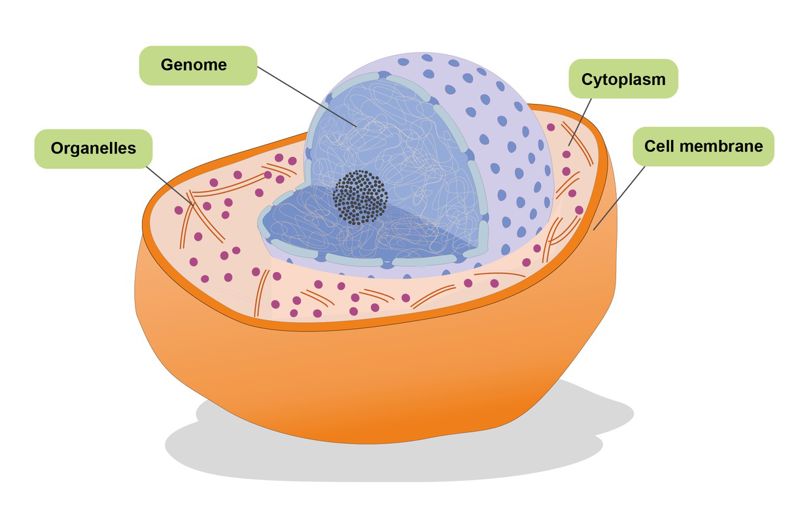
All living organisms are made up of one or multiple cells. Cells contain large amounts of water. Therefore, water is essential for all living cells.
Animal cells contain the following parts:
Plant cells are also made up of different parts:
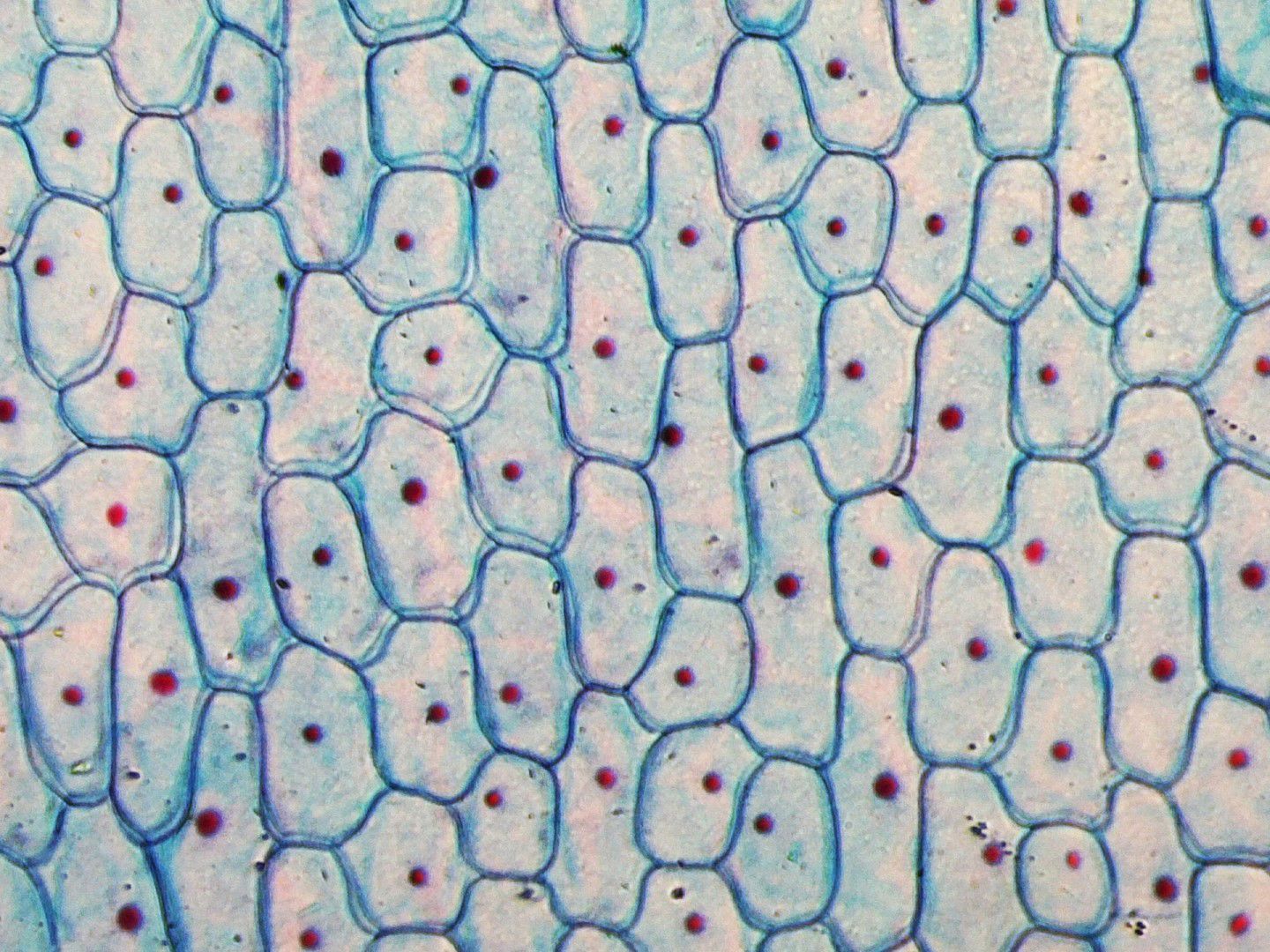
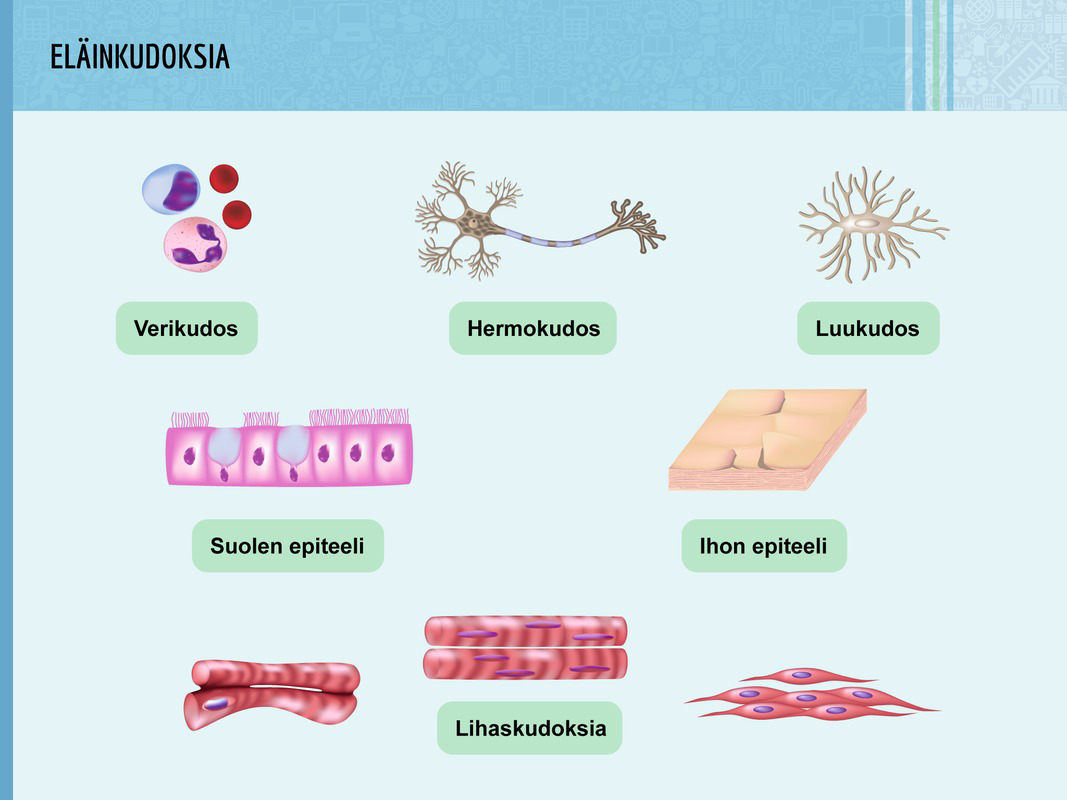
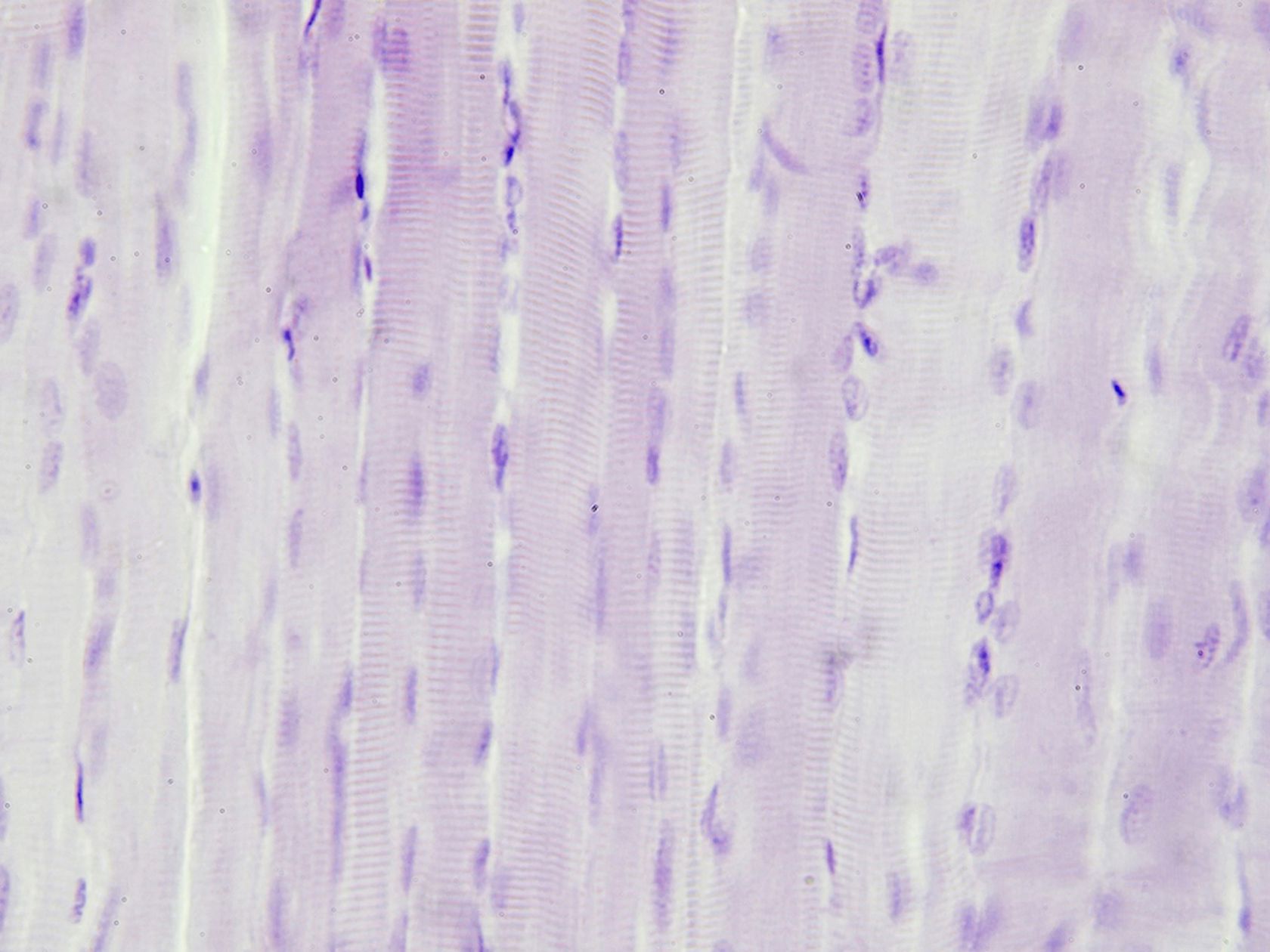
Both plant and animal cells can join together to form larger structures. These structures are known as cell tissues. For example, human muscle cells combine to form muscular tissue, whereas the superficial cells of a plant's leaves combine form superficial tissue.
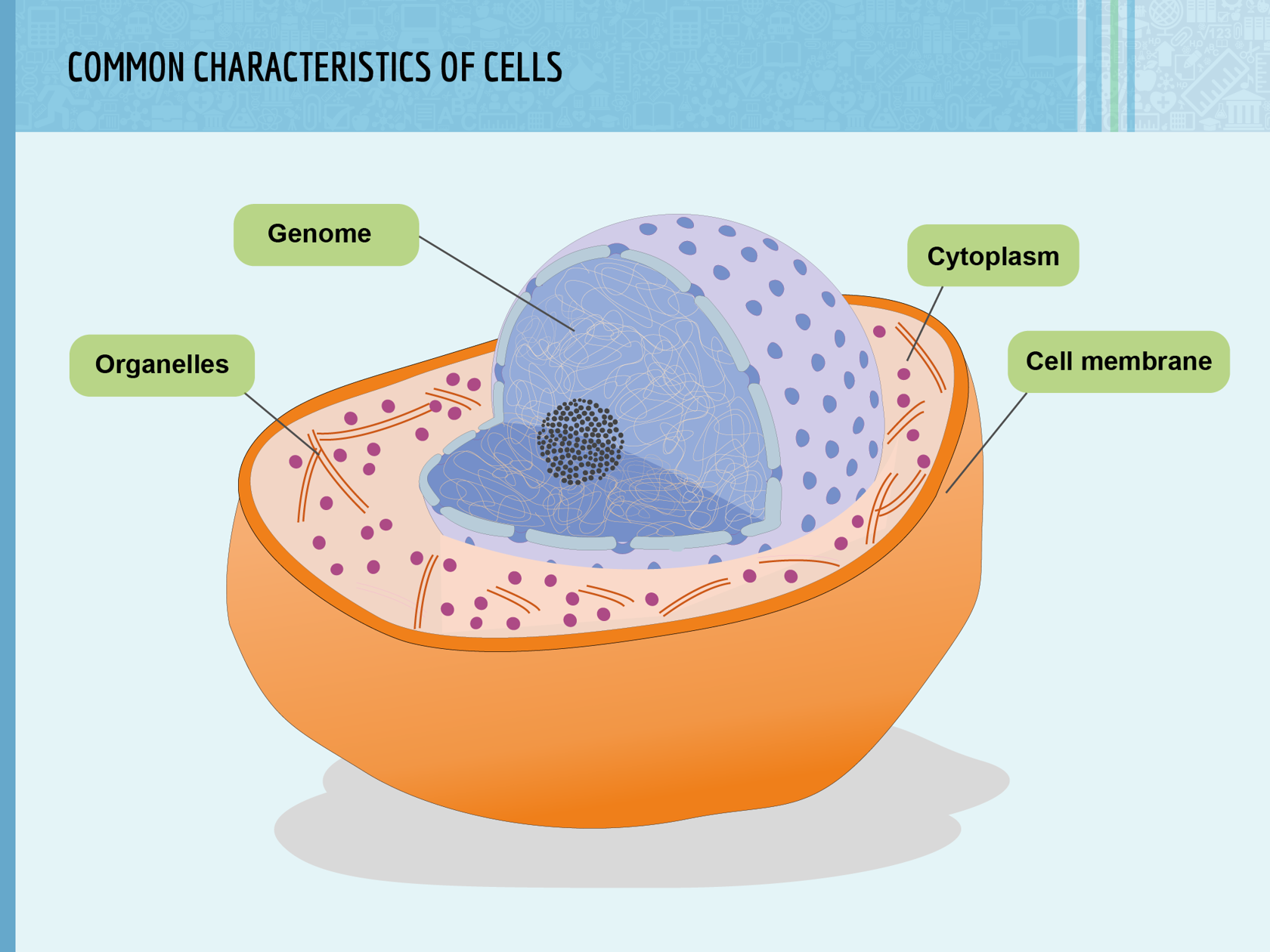
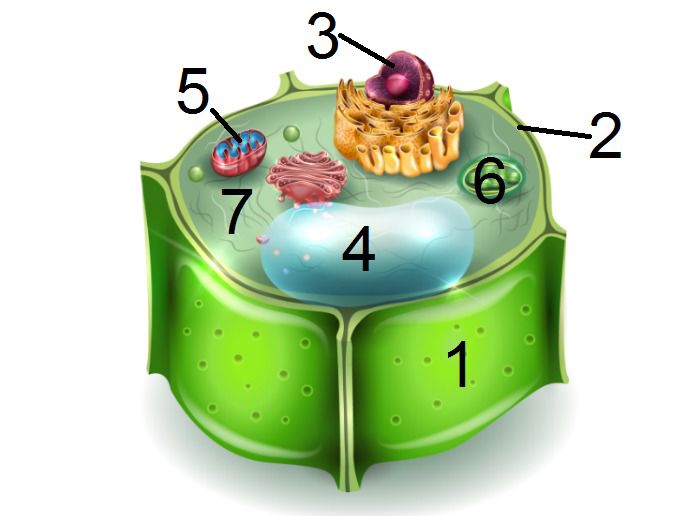
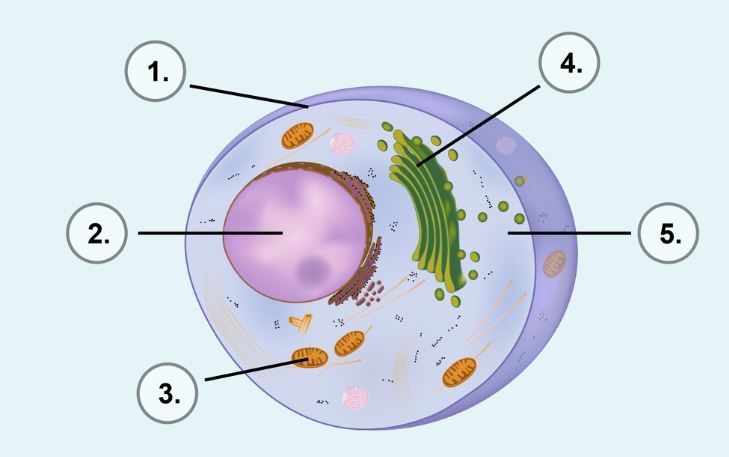
a) Cell wall
b) Cell membrane
c) Nucleus
d) Cytoplasm
e) Mitochondria
f) Vacuole
g) Chloroplasts
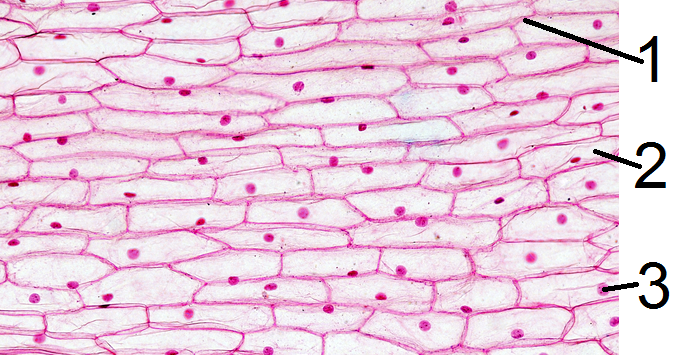
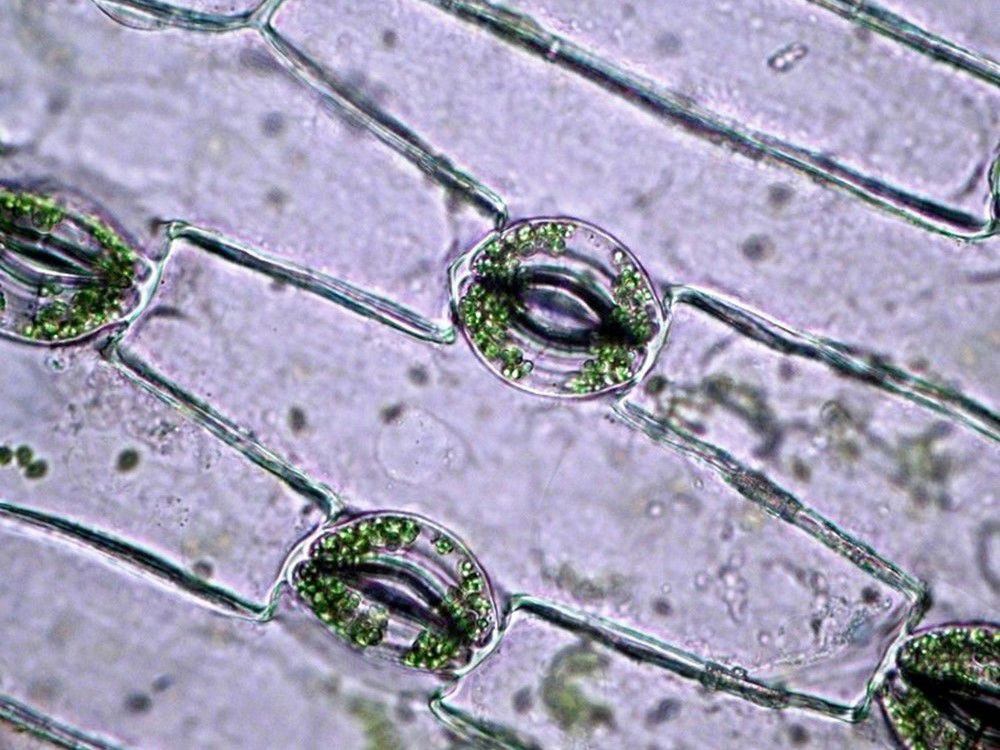
a) The microscopic image displays
b) The structure marked with the number 1 is called the
c) The structure marked with the number 2 is called the
d) The structure marked with the number 3 is called the

Mitä haluat tehdä tekstillä? Teksti käsitellään tekoälyn avulla, eikä sitä sen jälkeen muokata tai tarkisteta. Tekstissä voi esiintyä virheitä. Tarkista tekstin oikeellisuus vertaamalla sitä kirjan alkuperäistekstiin.
Valitse tiedostot, jotka haluat lisätä. Tuetut formaatit ovat txt, html, htm, pdf, odt, odp, ods, xls, xlsx, ppt, pptx, pps, doc, docx, rtf, png, jpg, jpeg ja gif.
| Nimi | |
|---|---|
| poista |
Huom.! Linkkien tulee alkaa ”http://”!
Opiq käyttää verkkosivun toiminnan, turvallisen käytön varmistamisen, käytön analysoimisen ja parhaan käyttömukavuuden tarjoamisen edellyttämiä evästeitä.
Eväste on käyttäjän tietokoneelta verkkosivun palvelimeen lähetettävä pieni tiedosto, joka sisältää verkkosivun toiminnan edellyttämiä käyttäjää ja hänen tekemiä valintoja koskevia tietoja.
Isoin osa evästeistä ovat Opiqin toiminnan kannalta välttämättömiä. Analyyttisistä evästeistä voi luopua ja silloin ei sinun käyttötietojasi ei käytetä Opiqin kehittämiseen. Lue lisää