Summer
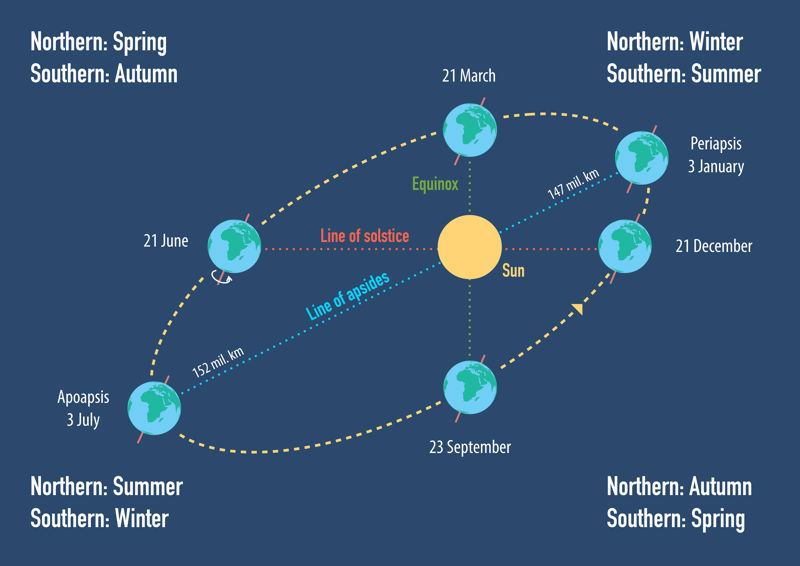
Summer is the warmest of the seasons. During the summer, the planet Earth is angled towards the Sun in a way that provides more sunlight to one hemisphere.
In the northern hemisphere, the summer months are June, July and August. In the southern hemisphere, the summer months are December, January and February.

- Temperature
- Snow
- Tides
- Wind
- Rain
- Aurora borealis
- The moon
- Clouds
The elements of weather
When talking about weather, we mean the following four things:
- temperature.
- clouds.
- rain.
- wind.
Together, these four things make up weather.
The picture on the right shows an approaching rain front. When this rain front comes even closer, the air temperature will drop, the sky will become cloudier, and the wind speed will often increase.
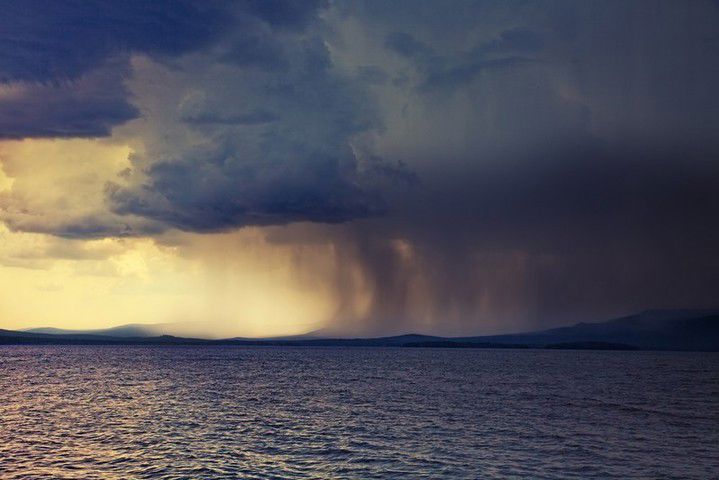

Weather factors
Temperature is a term that means how warm the air around us is. During the summer, the daily temperatures are at their highest, as the northern hemisphere receives more sunlight than during other parts of the year. Temperature is also affected by clouds and the wind.
Clouds prevent sunlight from warming up the planet's surface during the day. During the night, however, clouds act as a kind of blanket above the planet's surface, preventing heat from evaporating into space. This is why clear summer nights are colder than cloudy summer nights.
Air currents or winds have an effect on air temperature. When air flows from the north, it is usually colder than the air that flows from the south.
Near sea shores, the maritime climate makes the air temperature warm up more slowly during the spring than in inland areas. During the autumn, the maritime climate makes the air temperature cool down more slowly during the spring. This happens because the water of the sea warms up and cools down more slowly than land.
In inland areas, the continental climate results in a colder winter and warmer summer.
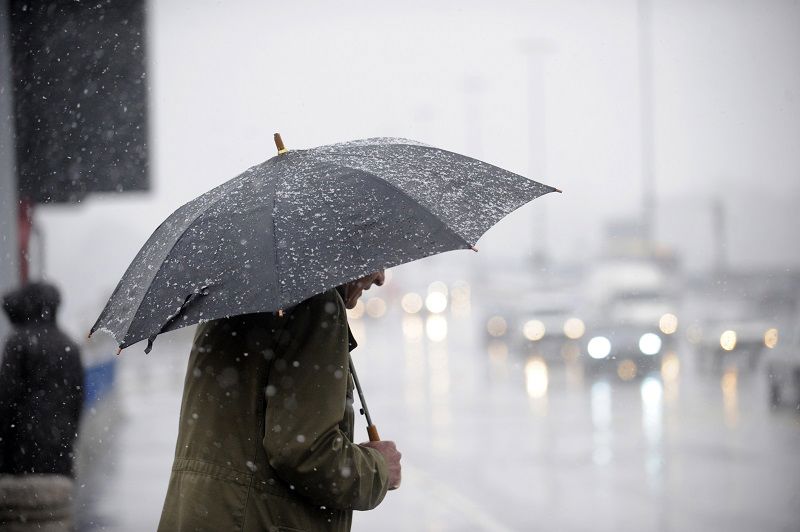


Rain

Rain is water that falls down to Earth’s surface from clouds. Clouds are formed when the Sun heats up the surface of a lake or a sea. When this happens, the water begins to evaporate and rise up, forming clouds. When the water vapour becomes condensed in the upper atmosphere, it forms small droplets that begin to fall towards the ground.
Normal rain can be either heavy or light. Usually, the raindrops are of a normal size, and the rain can continue for several hours without stopping.
In many regions of the world, there are certain seasons when it rains particularly heavily. In India, for example, from June onwards, big seasonal winds blow from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest and bring heavy rainfall to the area.
Rain is that falls down from clouds. When the Sun up the surfaces of bodies of water, the water becomes . It rises upwards in the atmosphere and forms .
When water vapour cools down in the upper atmosphere it is condensed into that begin to fall towards the planet's surface.
Wind
Winds are formed when the Sun warms up Earth’s surface and the air above it. The warm air begins to rise, and new air flows to fill the space left by it. This flow is the wind.
Winds often lower the air temperature, as the new air that flows to replace warm air is usually cold. The flow of air itself also has a cooling effect. You can try this yourself by blowing air on the back of your hand.
Winds can sometimes be dangerous, especially in shore areas. Storms can make trees fall down and cause damage to buildings. The scientists that focus on studying and predicting the weather, meteorologists, try to warn people about storms and other dangerous weather conditions by issuing wind and storm warnings. In the summer, storms are often connected to thunder showers.
Wind speed is measured in metres per second (m/s). This unit describes how many metres the wind travels during the course of one second.
Wind speeds
Speed (m/s) | Description |
0–3 | Weak wind |
4–7 | Intermediate wind |
8–13 | Swift wind |
14–20 | Hard wind (wind warning) |
21–24 | Storm (storm warning) |
25–28 | Heavy storm (storm warning) |
29–32 | Severe storm (storm warning) |
>32 | Cyclone, hurricane, tornado |
Lightning
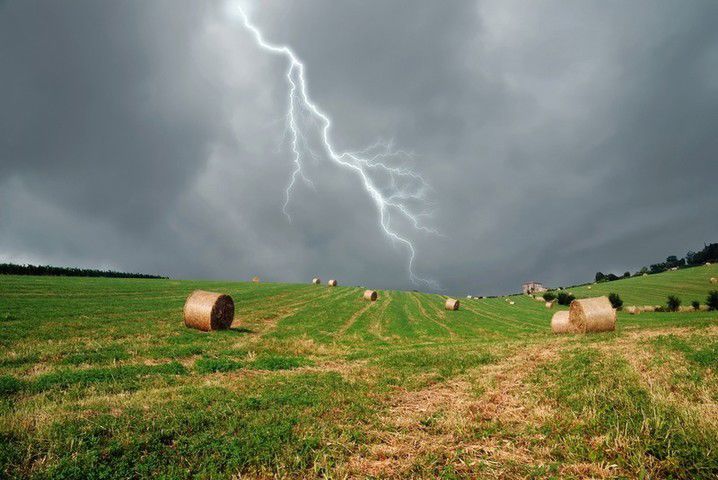

Lightning is a severe weather phenomenon where an electrical charge that has formed inside a thundercloud is released as a flash of light. Lightning can either hit another cloud or the ground.
During thunder and lightning storms, we often experience rain and heavy winds. The bolts of lightning that hit the ground can cause damage to trees, people and electrical equipment. Lightning tends to target tall objects, such as trees and tall buildings.
The sound of thunder can be heard for tens of kilometres, and the lightning can be seen even further away than that.
Why does the sound of thunder always arrive after the flash of lightning? This happens because sound travels more slowly than light. You can use this to measure the distance between yourself and the thunderstorm. If the lightning and the sound of thunder are separated by three seconds, the thunderstorm is located one kilometre from you.
Predicting the weather

Meteorologists are scientists that study and predict the weather. They make weather observations on different time scales and compare their observations with various weather prediction models. These models are based on weather data gathered over the course of long periods of time. Sometimes, weather can behave in unexpected ways and cause the prediction to be wrong.
Specialised equipment such as rain radars are used to make short-term weather predictions. Rain radars measure the movement of rain clouds and compare this with observations about wind speed. As a result, the meteorologist can predict when and where it will rain. These predictions are often quite reliable.
You can find meteorological weather predictions on the internet, in newspapers and on the radio and television. You can also try to predict weather yourself by making observations about various weather phenomena. For example, tall and dark clouds often indicate approaching rain fronts.
Test your knowledge
- 0–3 m/s
- 4–7 m/s
- 14–20 m/s
- 25–28 m/s
- 29–32 m/s
- > 32 m/s
- Weak wind
- Intermediate wind
- Heavy wind (wind warning)
- Heavy storm (storm warning)
- Severe storm (storm warning)
- Cyclone, hurricane, tornado
Calculate how far away the thunder storm is if the sound of thunder is heard 12 seconds after the flash of lightning.
It takes 3 seconds for sound to travel a kilometre.
The distance is seconds divided by .
Answer: The thunder storm is kilometres away.
Terminology
Summer weather
Term | Explanation |
summer | The season with the warmest and longest days of the year. In terms of temperature, summer is considered to begin when the average daily temperature exceeds +10 degrees Celsius. |
wind | The flow of air in the Earth's atmosphere. |
maritime climate | The climate type of shore areas, characterised by a mild winter and a temperate summer. |
continental climate | The climate type of inland areas, characterised by a warm summer and cold winter. |
lightning | A weather phenomenon where the electric charges of thunder clouds are released in the form of light. |
Summary
- Summer weather is most affected by temperature and rainfall.
- Winds and clouds can have a big impact on daytime temperatures.
- Weather can be predicted scientifically.
