Human geography

In the 7th grade, you studied natural geography[term: natural geography – The branch of geography that studies planet Earth and its natural phenomena.]. You learned how mountains are formed, what the vegetation zones of the planet are like, and how the planet's climate is changing.
In this course, we will examine geography from a different angle: from the point of view of humans. This branch of geography is called human geography[term: human geography – A field of geography that studies human activity and its relationship with the natural environment on different parts of the globe.].
During this course, you will learn things about Earth's populations, economies and cultural regions (such as nations and continents). As the natural conditions of the planet have a significant effect on many facets of human life, the course will also cover some topics of natural geography.
The course examines all the continents[term: continent – A large, unified mass of land. Earth's continents are North America, South America, Eurasia, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica.] of planet Earth that are inhabited by humans: Europe, Africa, Asia, Australia, North America and South America. Each continent will be examined by focusing on certain example nations. By focusing on specific nations, you will gain a better picture of how human cultures have adapted to their natural surroundings.
Test your knowledge
- population pyramids
- volcanic activity in Italy
- climate diagrams
- agricultural production in Italy
a. "The new world"
- Africa
- Asia
- South America
- North America
- Europe
b. The equator runs through these continents.
- Africa
- Asia
- South America
- North America
- Europe
c. Brazil
- Africa
- Asia
- South America
- North America
- Europe
d. Kenya
- Africa
- Asia
- South America
- North America
- Europe
e. Japan
- Africa
- Asia
- South America
- North America
- Europe
f. Spain
- Africa
- Asia
- South America
- North America
- Europe
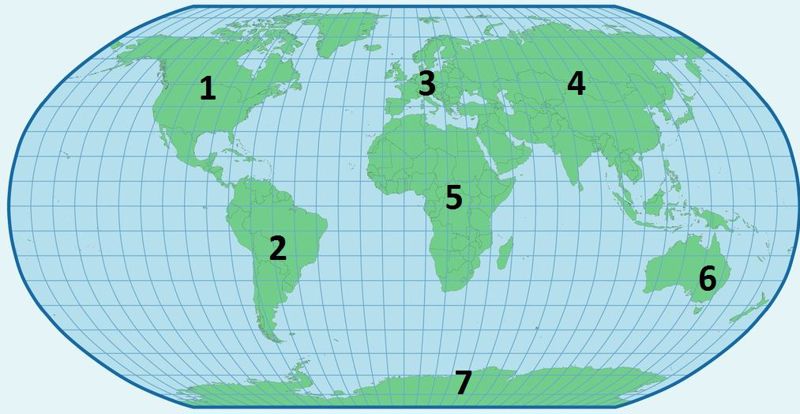
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
