Melting: from solid into liquid
When a block of iron receives enough heat, it will melt into liquid iron. This happens at the temperature of 1 500 degrees Celsius. As a liquid, this iron can then be poured into moulds. It will fill the moulds evenly, and its surface will be completely horizontal.
Mercury is a metal that melts at a temperature of -40 degrees Celsius. This means that it is already a liquid at room temperature. Mercury has traditionally been used in thermometers.
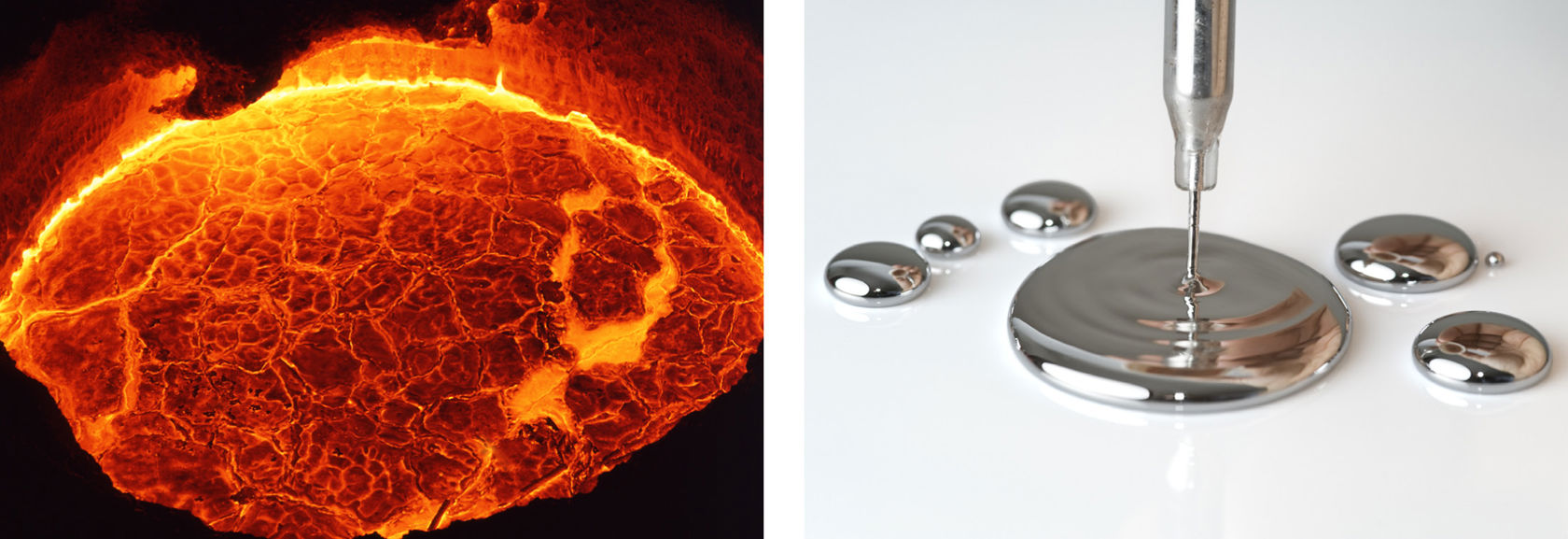

Image on the right: Mercury is a metal that exists in a liquid state at room temperature.
Similarly, when a block of ice receives enough heat, it will melt into liquid water. The melting point of ice is 0 degrees Celsius. The block of ice retains this temperature as long as it is melting.
If you could see individual atoms, you would notice the difference between solid and liquid matter at the atomic level. In solid matter, the molecules that make up matter are packed tightly and do not almost move at all. When heat is increased, the molecules begin to move. Eventually, they will detach from one another and flow into a liquid.
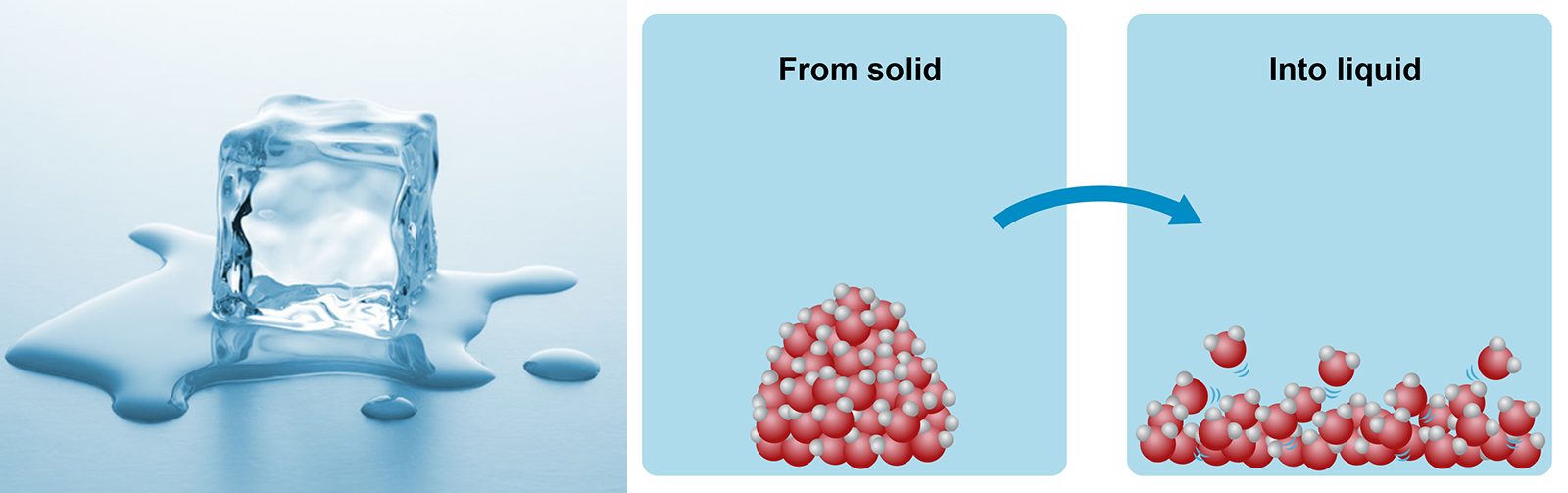
Image on the right: When a solid block of ice melts into a pool of liquid water, the movement of the molecules increases.
Evaporation: from liquid into gas
When liquid iron receives more and more heat, it begins to boil and evaporate into iron gas. Iron gas cannot be photographed because gas is invisible. The boiling point of iron is almost 3 000 degrees Celsius.
Similarly, when heat is applied to liquid water, it will begin to evaporate into an invisible gas we call water vapour. It is possible for us to see hot clouds of steam rising from the pot in which water is boiled. This steam is not water vapour, but instead consists of small droplets of liquid water. Eventually, these droplets will also evaporate into invisible water vapour.
Image on the right: When heat is applied to liquid water, it begins to evaporate into invisible water vapour.
When water boils, it evaporates into gas even at the bottom of the pot. Water vapour can be seen rising through liquid water in the form of bubbles. The normal boiling point of water is 100 degrees Celsius.
If you could see things at an atomic level, you could see how the molecules that make up liquids cling to one another while moving. When more heat is applied to the liquid, the molecules begin to move more and more. Eventually, the molecules will detach from one another completely, bumping into each other at great speed.
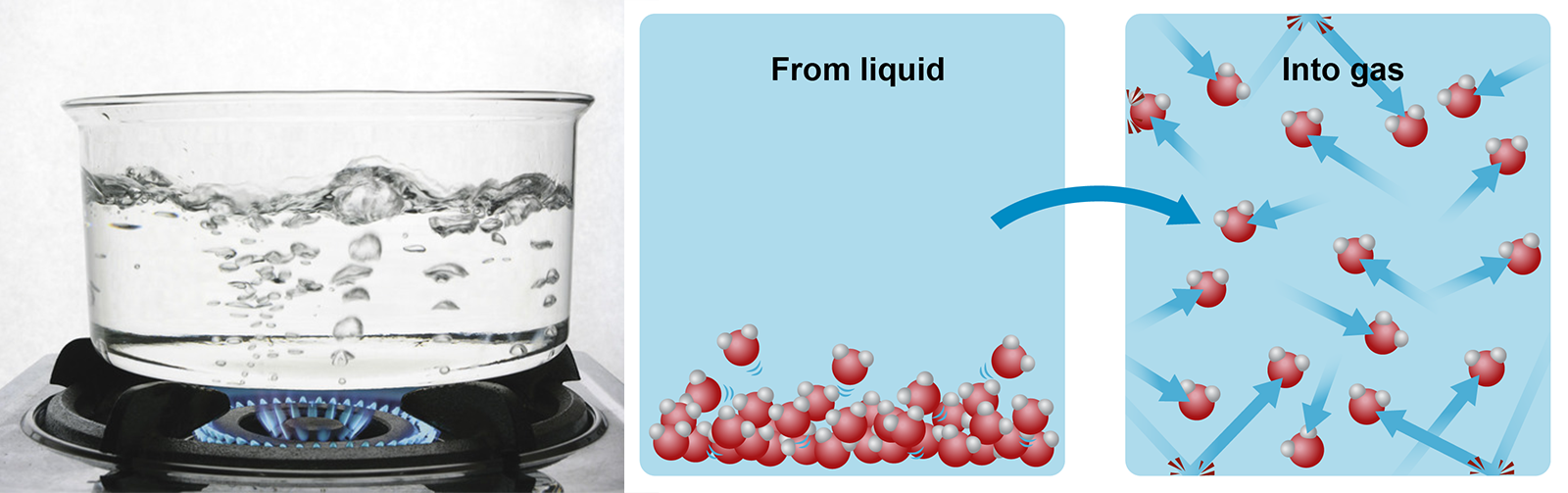
Image on the right: When heat is increased, the amount of molecular movement also increases.
Condensation: from gas into liquid
When you breathe air out of your lungs, a large amount of water will also travel with your breath. You cannot see this water because it is in its invisible, gaseous form. When the weather is cold, the water vapour in our breath condenses into small, liquid droplets, forming a cloud of fog. You can see this cloud of fog only for a short while. Similarly, if you breathe on a cold window glass, the water vapour in your breath will temporarily condense on the glass, making it appear foggy.
Water also condenses high up in the sky because the temperatures in high altitudes are cold. Small fog or cloud droplets can be seen forming clouds in the sky. The water droplets condense on the surfaces of small dust particles in the atmosphere. If you follow the movement of clouds for a long time, you can see some of them grow. This happens when humid air arrives near them from below. Other clouds will grow smaller, as their water droplets evaporate into water vapour.
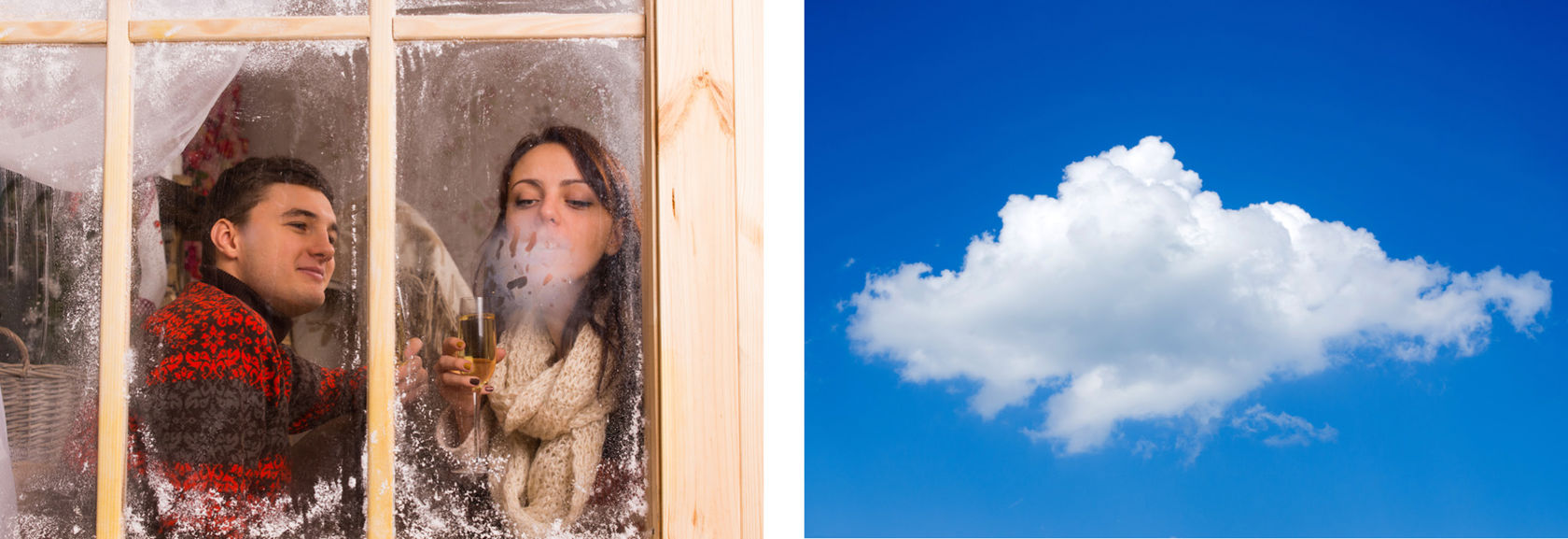

Image on the right: Water vapour condenses into liquid droplets when the temperature is cool. These small droplets of water form the clouds you see in the sky.
Air is a gas. If you wanted to condense air into a liquid, you would have to remove a large amount of heat from it. The condensation point of air would be somewhere near -200 degrees Celsius. Air is a mixture of gases that is mainly made out of nitrogen and oxygen. Liquid oxygen is used in space shuttles, whereas liquid nitrogen is used to freeze things quickly. In the image below, you can see a cook creating instant ice cream with the help of liquid nitrogen.
If you could see things at an atomic level, you could perceive gas molecules moving everywhere in the air around you. In a closed container, the molecules of a gas will bump into one another and the edges of the container. This movement increases when the heat is increased. Conversely, when the amount of heat is decreased, the movement of the molecules becomes slower. Eventually, the molecules will cling on to one another and begin to move at a slower speed. When this happens, the gas condenses into a liquid.
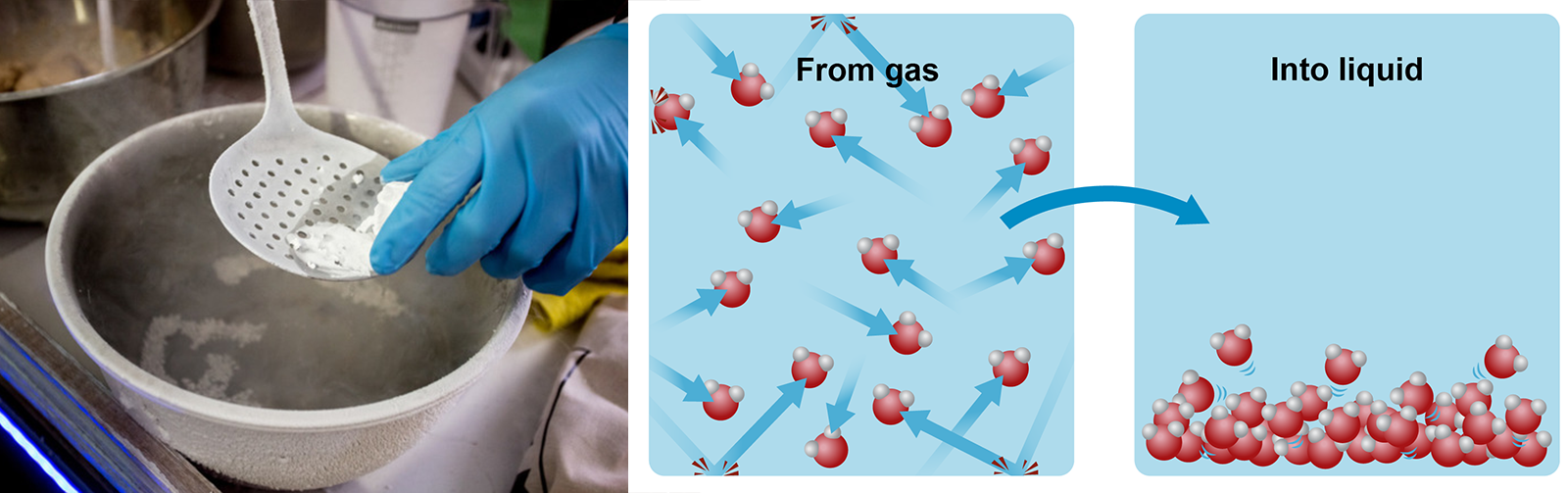
Image on the right: When the temperature of a gas is decreased, the movement of its molecules becomes slower.
Solidification: from liquid into solid
When liquid iron loses heat, it will begin to solidify. Molten, liquid iron can be poured into moulds, and when the iron cools down and solidifies, the result is a block of iron shaped like its mould (image on the right).
Similarly, when liquid water cools down, it will solidify into solid water. In other words, it will freeze into ice, snow or hail.
If you could see things at an atomic level, you could observe how the molecules of liquid matter move slowly. When the liquid cools down, the molecules will begin to move slower and slower, before eventually stopping almost completely. When this happens, the molecules will cling on to one another tightly: the liquid matter has transformed into a solid matter.
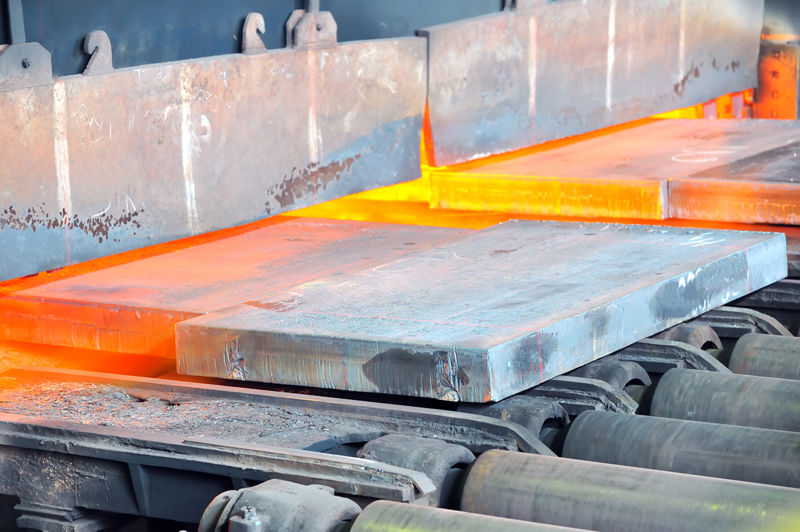

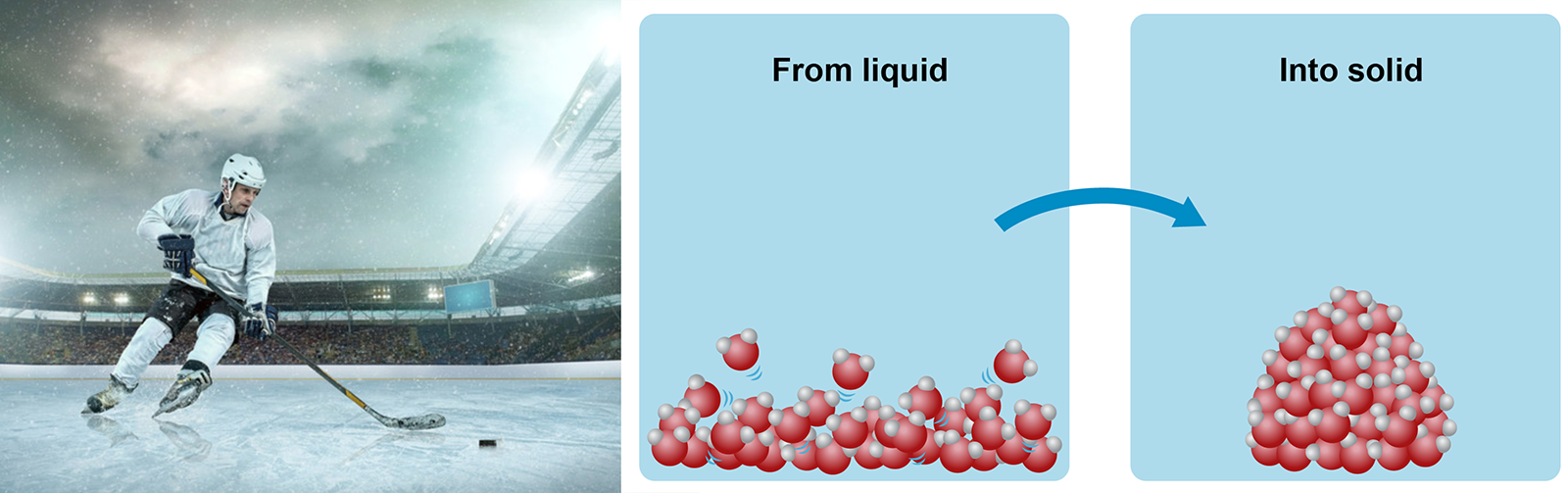
Image on the right: When liquid water cools down, the molecules begin moving slower and slower. The molecules will cling on to one another tightly, and eventually stop moving altogether. When this happens, the water has solidified into ice.
Terminology
States of matter
Term | Explanation |
melting | A process where solid matter transforms into liquid matter as its temperature increases. E.g. ice → water. |
evaporation | A process where liquid matter transforms into gaseous matter as its temperature increases. E.g. water → vapour. |
condensation | A process where gaseous matter transforms into liquid matter as its temperature decreases. E.g. vapour → water. |
solidification | A process where liquid matter transforms into solid matter as its temperature decreases. E.g. water → ice. |
Summary
- The three states of matter are solid, liquid and gas.
- The most common state changes are melting, evaporation, condensation and solidification.
